What is an output of Bioinformatics?
Contents
What is an output of Bioinformatics?
Madina Seidualy
Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology
Abstract
Everything in the world functions by following laws of programming: input, function, output. Life itself compile their own program. Input file of the Life software is DNA, essential for all known forms of life, then do transcription and translation, as an output comes out protein, functional block of life. The whole those process is only input of the Bioinformatics program. During the runtime, it interprets DNA, transcriptomes and proteins, and does analyze, compare and predict genes, protein structure and molecular function. Then what is the output of Bioinformatics? The main output would be AI computer program, which will replace all medical doctors of the Earth. This AI store all acquired information from analysis and will suggest treatment for every patient, even do surgery.
Introduction
Biology aims to understand what life is. The essence of life is information processing. Bioinformatics is the study of life forms using informatics methods and the key to life science. The main difference from other Informatics Science, Bioinformatics hack life information!
Life itself compile their own program. Input file of the Life software is Genome, where whole functional information is coded. It is worth to mention that DNA confers all of the information the organism needs to function and for the next organism to grow and develop. While program run, firstly, it goes through DNA, transcribes, translates and as an output file generates proteins, which conduct main functions of the Life. Moreover, the generated protein from life programming script, recognizes a particular element or another protein as an input, and apply functions like transition or addition a phosphor group, consequently for output produce altered form of the input substance. Everything in the world functions in the same series of mechanisms of input, function, output. Admittedly, Bioinformatics also!
The input file for it is the whole program of life, all the processes that take part in the living cell will be the main information source for Bioinformatics. However, there is a question like what is the output of this Bioinformatics program? Is only responsible for reading the Life information or only for analyzing? In this essay, I will provide with current purpose and products of the Bioinformatics field, also emphasize main its main actionable application in the future plan.
Result
Bioinformatics scientists study and dissect massive amounts of data sets at the molecular level such as proteomics, raw microarray, and genomic sequence data.
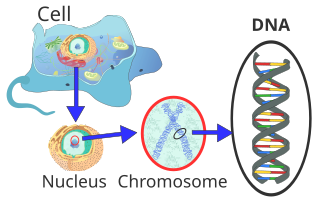

Thereby, the input of Bioinformatics is living organism's DNA, mRNA or protein and output is a text-based file, which human can read.
Through bioinformatics technology, a string of molecules can be extracted from a database and displayed on a computer screen as a series of letters. As a result, the purpose of the Bioinformatics here is alteration the format of information flow.
After gathering all life information, Bioinformaticians decipher them by designing web-based informatics tools.
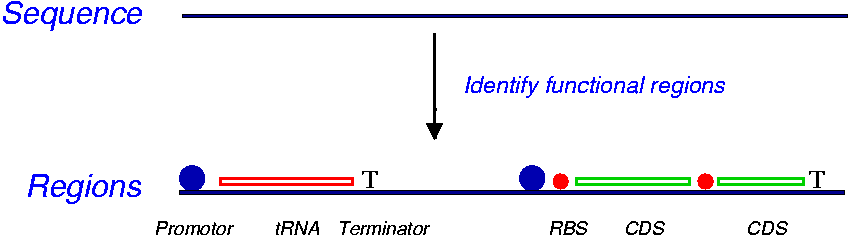

In this process, the acquired series of letters compare and contrasted among human and animal samples as a method of finding out how similar or different particular genes or proteins to other animals and how that might help develop new drugs in order to cure life-threatening diseases. Now Bioinformatics scientists start to translate meaning and importance of gene and proteins to the language that people can understand and analyze.
I can conclude partially that Bioinformatics is a compiler, that translates source code into object code, read molecular information blocks and interprets them to the humanity.
It has not escaped our notice that Bioinformatics is also directly related to seeking new treatments for diseases. The folowing image summorizes all schematic outlining of how scientists can use bioinformatics to aid rational drug discovery.
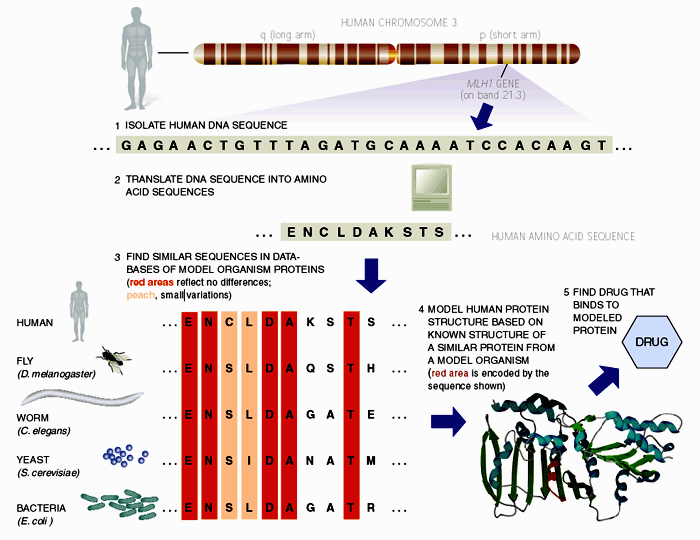
Discussion
All inventions and discoveries in the Bioinformatic field are either about new sequenced or identified protein or some species sequences or tools with algorithms for calculating or comparing massive amounts of genomic data. After having all genomes. proteins, and transcripts catalog, what would be the next step?
The science of bioinformatics — the computer systems that extract the information that researchers use to find disease cures and open other new worlds — has been around since the 1960s, according to Dr. Susan Smith, a professor and research biologist at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, in Troy, NY. From that period the output of the Bioinformatics actively used in the medical applications. However, in future, the real output of Bioinformatics would be AI computer program, which will scrutinize genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics related to the patient and recommend corresponding treatments and medicine. This invention will replace the majority of hospital work. Even there will be AI that will do surgery, or repair any mismatch in the human genome. In the end, there would no necessity of the doctors in society.
In a nutshell, the main output of the Bioinformatics is a DoctorAI. The narrow computer programs actively used nowadays in Biological Science are just functions of Bioinformatics, not the main yield. To compare, in the script of the central dogma program the principal input is DNA, and the product is protein. Nevertheless, there are minor intermediate programs such as running of the transcription and translation. If following the same trend, Bioinformaticians on the way of compiling the program, there is no output yet. The big picture of it will be, input <Living process information> running output <DoctorAI>.
Reference
- Steve Starger. “What is Bioinformatics?” Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) Recited from: http://www.rpi.edu/academics/interdisciplinary/what_is_bioinformatics.html
- “IntroductionToGenomics” Article from: https://wiki.cebitec.uni-bielefeld.de/brf-software/index.php/GenDBWiki/IntroductionToGenomics
- “The roots of Bioinformatics Theoretical Biology” PLOS Computational Biology, Vol. 7, No. 3. (31 March 2011), e1002021, doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002021 by Paulien Hogeweg posted