Difference between revisions of "KSH 0611 Review Epigenetic modifications regulate gene expression"
From Biolecture.org
imported>Seung-hoon Kim |
imported>Seung-hoon Kim |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
<h2>Definition : Heritable changes in gene activity and expression that occur without alteration in DNA sequence</h2> | <h2>Definition : Heritable changes in gene activity and expression that occur without alteration in DNA sequence</h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Different cells control switching on and off in different genes</h2> | ||
<h2>Two well-known epigenetic modifications</h2> | <h2>Two well-known epigenetic modifications</h2> | ||
| − | < | + | <ul> |
<li>Chemical modification to the cytosine residues of DNA (DNA methylation)</li> | <li>Chemical modification to the cytosine residues of DNA (DNA methylation)</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><img src="http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/methylation/dna_mdna.png" /></p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ul> | ||
<li>Histone modification</li> | <li>Histone modification</li> | ||
| − | </ | + | </ul> |
<h2>Why is it important ? >>> Epigenetic modifications regulate gene activity and expression during development and differentiation, or in response to environmental stimuli</h2> | <h2>Why is it important ? >>> Epigenetic modifications regulate gene activity and expression during development and differentiation, or in response to environmental stimuli</h2> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 41: | ||
<h4>We could increase the mRNA of <em>ADH</em> and then make ADH more than usual when we drink much </h4> | <h4>We could increase the mRNA of <em>ADH</em> and then make ADH more than usual when we drink much </h4> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Only 2 % of human genome encodes protein and the other 98% controls gene expression by epigenetic mechanism.</h2> | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
Revision as of 13:44, 11 June 2016
Contents
- 1 Epigenetics
- 1.1 Definition : Heritable changes in gene activity and expression that occur without alteration in DNA sequence
- 1.2 Different cells control switching on and off in different genes
- 1.3 Two well-known epigenetic modifications
- 1.4 Why is it important ? >>> Epigenetic modifications regulate gene activity and expression during development and differentiation, or in response to environmental stimuli
- 1.5 Epigenetics is considered a bridge between genotype and phenotype
- 1.6 Explain how cells carrying identical DNA differentiate into different cell types >>> Epigenetics
- 1.7 Epigenome - global analyses of epigenetic markers across the entire genome
- 1.8 Chromatin - Histone protein / DNA complex in eukaryotic cells
- 1.9 How to regulate Protein Synthesis - Epigenetic inheritance controls the amount of the transcribed mRNA. Thus, protein production is regulated.
- 1.10 Only 2 % of human genome encodes protein and the other 98% controls gene expression by epigenetic mechanism.
Epigenetics
Definition : Heritable changes in gene activity and expression that occur without alteration in DNA sequence
Different cells control switching on and off in different genes
Two well-known epigenetic modifications
- Chemical modification to the cytosine residues of DNA (DNA methylation)
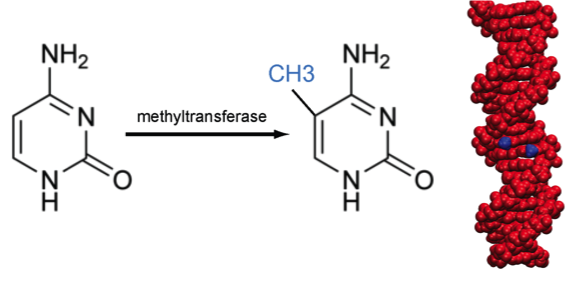
- Histone modification
Why is it important ? >>> Epigenetic modifications regulate gene activity and expression during development and differentiation, or in response to environmental stimuli
Epigenetics is considered a bridge between genotype and phenotype
Explain how cells carrying identical DNA differentiate into different cell types >>> Epigenetics
Epigenome - global analyses of epigenetic markers across the entire genome
Chromatin - Histone protein / DNA complex in eukaryotic cells
Basic Unit - nucleosome - 146 bp of DNA wrapped around an octamer of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4)
- Euchromatin - transcriptionally active state - the region where DNA is accessible due to the relaxed state of nucleosome arrangement
- Heterochromatin - transcriptionally inactive state - the area where DNA is packed into highly condensed forms that are inaccessible to transcription factors
How to regulate Protein Synthesis - Epigenetic inheritance controls the amount of the transcribed mRNA. Thus, protein production is regulated.
Ex) Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) breaks down alcohol in liver cells.
We could increase the mRNA of ADH and then make ADH more than usual when we drink much
Only 2 % of human genome encodes protein and the other 98% controls gene expression by epigenetic mechanism.